Verifications
Checking definitions and availability of online services
- Security Services - IronPort Anti-Spam
- Security Services - Services Overview
- Security Services - IMS and Graymail
- Security Services - Sophos
- Security Services - Outbreak Filters
- Security Services - SenderBase
Reports
- Monitor
The ESA contains a large number of reports. Some can be scheduled and emailed to us in Monitor - Scheduled Reports. The basic view is on the Dashboard. In the Monitor menu, there are reports from various areas, often with links to more detailed reports, or with tabs to switch between them.
Adding an accepted domain
- Mail Policies - Recipient Access Table (RAT)
If we have a new domain for which we want to receive mail, we need to add it to the Recipient Access Table (RAT).
- Network - SMTP Routes
If we have defined routing of individual domains to an internal mail server (perhaps not using the general All Other Domains), we also need to create a record in the SMTP Routes.
Message queue and forced delivery
- Monitor - Delivery status
The item Active recipients means that messages for this domain are in the queue. We can expand the domain and choose Retry Delivery.
Resolving undelivered messages
The most common area from practice is finding out why a message was not delivered, and possibly setting up some exception on the AntiSpam. The ESA can reject or block a message at various services, and the response varies accordingly.
- IP Reputation - Host Access Table (HAT) - when establishing a connection to the Listener, the source address is checked using the HAT
- Recipient Access Table (RAT) - check of the recipient address (I didn't find when it's performed)
- Incoming Mail Policies - a number of checks are performed within the policy (if enabled for the given recipient/sender)
- Message Filters
- Anti-Spam
- Content Filters
In some cases, for example IP reputation, the incoming connection is rejected and the sending server is normally given information that is delivered to the sender in the email. When a message is identified as Spam, it is deleted or placed in quarantine according to the policy. The sender doesn't receive any information, the recipient only if we use quarantine and send a report.
As an administrator, we have several options to search for an undelivered message. The information is in the following chapters.
Tracking messages - Message Tracking
- Monitor - Message Tracking
We need to have this feature enabled. Then we can enter some parameters of the message we are looking for, primarily the sender's email address and time interval. The found items are displayed, where we see the LAST STATE, which usually says whether the message was delivered to the target mail server, or placed in quarantine. We can also click on Show Details and a window with detailed logs will be displayed.
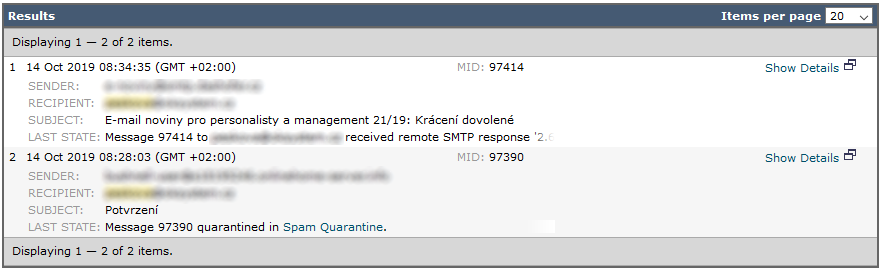
If the message is not found, it is likely that the connection from the source IP address was already blocked, and therefore we don't have information about the message details.
Checking reputation - sender receives an error
On the https://www.talosintelligence.com/ website, we can find the reputation of a domain or IP address.
If the incoming connection (source IP address) has a poor reputation, the connection is normally rejected. The message the sender wanted to send does not then reach the recipient's quarantine, nor can we easily find it in the log. The sending mail server receives an error, which is usually delivered as a response to the sender.
mail.company.com: 554-mail.company.com 554 Your access to this mail system has been rejected due to the sending MTA's poor reputation. If you believe that this failure is in error, please con tact the intended recipient via alternate means.
In such a case, we can verify that the sending address/domain has a poor reputation on the Talos website. The problem is how to determine the IP address from which the message was sent. For the sender's domain, we can look up the MX record in DNS, but that is primarily the address for receiving mail for that domain, the sending address may be different. If there is a textual SPF record in DNS, we can find the address from which the mail should be sent.
If we enter the domain on the https://www.talosintelligence.com website, the mail server according to the MX record will also be found. If we enter the IP address, the IP addresses that send mail for that subnet are listed.
Message Tracking - searching for a rejected connection from a given IP address
If we have enabled logging of rejected connections (Save tracking information for rejected connections) when Enabling message tracking, we can use Message Tracking.
- Monitor - Message Tracking
- expand Advanced
- enter the IP address in Sender IP Address/Domain/Network Owner
- and select Search rejected connections only
- select the required time interval and run Search
If we don't save rejected connections, we can still look in the log, see the next chapter.
Viewing logs - searching for a rejected connection from a given IP address
If we need to see the logs about mail processing directly, we can either download the text file, or connect to the CLI (usually via SSH) and use commands to display them.
Download log file
- System Administration - Log Subscriptions
- select the required log (now
mail_logs) and click on the name in the Log Files column - click on the file name by date to start the web download
Searching logs in CLI
Display the last ten entries and all current ones.
tail mail_logs
Searching using the grep command itself and a guide or by entering the command with a regular expression for searching. We can simply enter a time (the command above will show how it's stored), e.g. Mon Oct 7 13:15 and any other text.
grep -e "Mon Oct 7 13:15.*" mail_logs
Setting exceptions - Safe Senders, Whitelist
If we have identified where the incoming message is blocked, we can set an exception so that the filtering does not occur and the message is delivered next time. The most common is to add the sending IP address to the HAT or the sending email to the policy that does not perform AntiSpam checks. If we use quarantine, users can set certain exceptions themselves. Alternatively, we can report incorrectly classified messages to Cisco.
Below is just an example of how setting an exception for an email address or IP address can look simple and intuitive in the Symantec Messaging Gateway implementation. A complicated Cisco solution is also briefly described.

Sender IP address
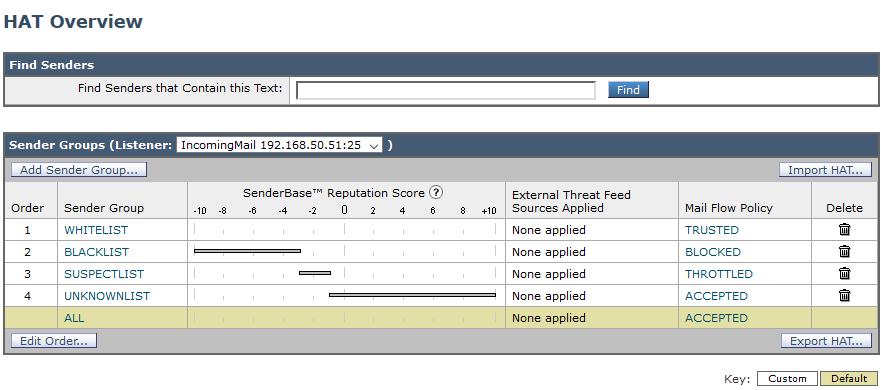
- Mail Policies - HAT Overview - WHITELIST
For each Listener, we define rules that determine the remote hosts (IP addresses of senders) that are allowed to connect. The Host Access Table (HAT) is used for this. The SenderBase Reputation Service is typically used here, so some IP addresses are blocked based on reputation.
If we have a trusted sender, in the style of a mail server, we can enter its IP address into the WHITELIST group, where the TRUSTED policy is applied. These senders are not checked either by IP reputation or the AntiSpam engine (but the AntiVirus check is performed).
Sender email address
- Mail Policies - Incoming Mail Policies
If we want messages from a certain email address not to be marked as Spam (their check not performed), the only solution is to create a special Incoming Mail Policy in the style of Safe Sender Emails or Skip AntiSpam Scan. We create a policy that we place at the beginning of the list. We add users to the policy - Add User, here we can specify the recipient and sender using the exact address or just the domain. On the policy, we disable the Anti-Spam function, and possibly others.

Note: In the same way, we can define recipients who will receive all messages (AntiSpam check is not performed for them).
Recipient email address
- Mail Policies - Recipient Access Table (RAT)
The main decision on whether an address will be accepted is made using the Recipient Access Table (RAT). Here we can set entire domains or individual email addresses, and determine whether they are accepted or rejected. Or set Bypass Receiving Control. Even when we set an address to be accepted, the AntiSpam check is still performed.
The domain company.com will cover email addresses on this domain, and we can also define all subdomains .company.com.
Exception from Sender Domain Reputation
- Security Services - Domain Reputation - Domain Exception List
If we use SDR, we can specify certain domains for which the check should not be performed.
Exceptions from Sender Verification
- Mail Policies - Exception Table
If we use Sender Verification, we can define exceptions.
Safe senders per user
- Spam Quarantine - Options - Safelist
In the quarantine, each user can manage their own Safelist and Blocklist. The administrator can edit them for all users.
Reporting incorrectly classified messages to Cisco
In the quarantine settings, we can allow a message to be sent to Cisco for analysis when released from the quarantine (when it is delivered to the user). But the main solution when we want to inform Cisco about the incorrect classification of a message is described in Reporting Incorrectly Classified Messages to Cisco.
This means registering on the Submission and Tracking Portal. We link the account with our appliance in System Administration - Email Submission and Tracking Portal Registration. Then we have to register our domains. After that, we can use the Outlook plugin, the above-mentioned portal, or send messages as attachments to special addresses.
There are no comments yet.