Note: I practically installed Exchange Server SE role Mailbox server on Windows Server 2025. In an environment with different internal and public DNS domain and Split DNS (Split-Brain DNS). Into existing Exchange 2016 organization using DAG (Database Availability Group).
Moving Mailboxes
During Exchange organization migration to a new version and new servers, we must first configure the new servers. Then follows the step where we move mailboxes to new databases on new servers. Moving a mailbox from one mailbox database to another is a common simple process. It's called a Move Request and can run online. It uses Mailbox Replication Service (MRS).
Moving mailboxes takes some time, which depends on their quantity and size. In practice, gradual moving can take us several weeks. It can run online and I haven't encountered any problems. But it might be more efficient to perform outside working hours when no client is connected to the mailbox.
Moving mailboxes loads mail servers, but Exchange monitors the load and pauses moves. The request status for the move then shows instead of CopyingMessages for example StalledDueToTarget_MdbReplication, StalledDueToTarget_DiskLatency, StalledDueToTarget_Processor.
IMPORTANT Mailbox move runs as standard transport, so transaction logs are created for the entire content. During migration we need a lot of space to store these logs. Therefore the log disk must be much larger than for normal operation. If space runs out, the database gets disconnected. When using DAG, the same space is occupied on all servers where database copies are located.
Mailbox Move Order
Microsoft states the following order for moving different types of mailboxes.
- move system mailboxes (arbitration mailboxes)
- move user mailboxes (user mailboxes)
- move public folder mailboxes (public folder mailboxes)
Note: I came across a recommendation to move public folder mailboxes first before moving user mailboxes. The stated reason was that otherwise there's no access to public folders in OWA (which is done through favorites - Favorites). For my moved test user, access to PF on original servers worked.
We Can Move
- one mailbox (Move Request)
- multiple mailboxes (Batch Move Request)
- multiple mailboxes specified in CSV (Migration Batch)
How to Move Mailboxes
Mailbox moves can be managed (configured) in EAC (Exchange Admin Center), where a simple wizard is available. Or using EMS (Exchange Management Shell), where we can easily perform bulk configurations. A job (batch - Batch) is created that performs the move and runs in the background. EAC always creates a Migration Batch. When we create a Migration Batch in EMS, we can see it in EAC and control it.
Migration Batch takes a CSV file as input and performs moves of all specified mailboxes. It generates a Move Request for each one. The batch can start immediately after creation or manually. In EMS we can use parameters CompleteAfter and/or StartAfter for both batch (Batch) and request (Request), which determine the date and time for completion or start of data migration.
After successful completion of the move, it's good to delete the request. Microsoft states this is no longer needed (apparently because automatic deletion occurs after 30 days). But if we wanted to move the mailbox again, it wouldn't allow us because it has an assigned completed move request. On the other hand, this can be an advantage so we don't accidentally move a mailbox that has already been moved.
Exchange Admin Center (EAC)
- EAC - Exchange Admin Center
- Recipients - Migration
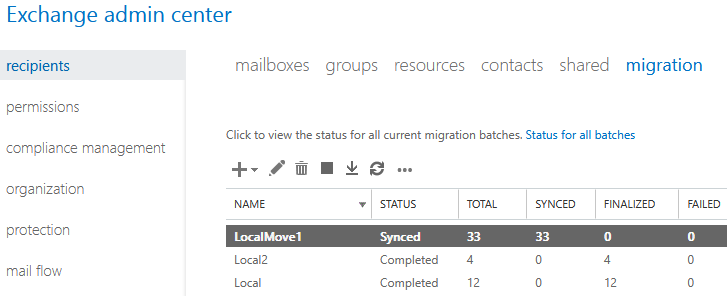
- click on plus (New) and choose Move to a different database
- add mailboxes (users) we want to move (by selecting from list or using CSV)
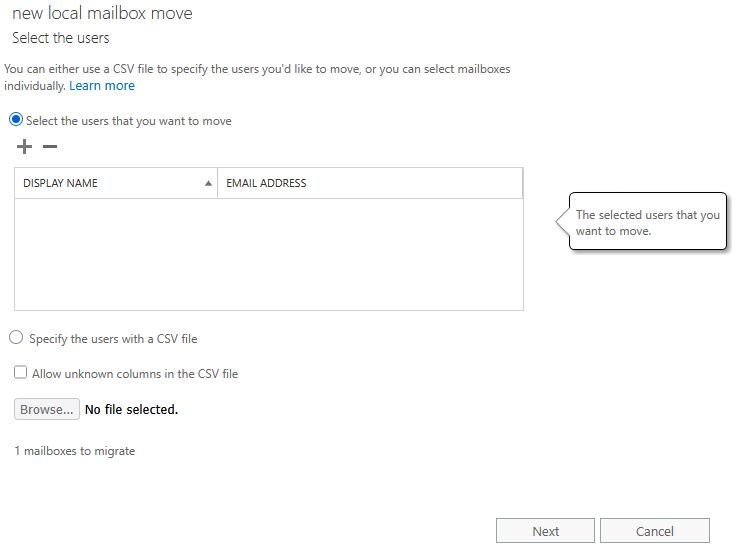
- in the second step name the job (batch), choose target database, optionally also archive database and bad item limit
- in the last step set completion report recipient and whether the batch starts and ends automatically or manually
Exchange Management Shell (EMS)
We have various PowerShell cmdlets available such as
- New-MoveRequest
- New-MigrationBatch
- Get-MoveRequest
- Get-MigrationBatch
- Remove-MoveRequest
- Get-MoveRequestStatistics
- Get-MailboxStatistics
Mailboxes
- Exchange Server 2016 moving mailboxes and OAB - my older article
Moving System Mailboxes
First, it's recommended to move Arbitration Mailboxes, which are system mailboxes where various organization-wide data is stored. Below is a list of seven Arbitration Mailboxes and one Audit Log Mailbox.
DisplayName Name
----------- ----
Microsoft Exchange SystemMailbox{bb558c35-97f1-4cb9-8ff7-d53741dc928c}
Microsoft Exchange Approval Assistant SystemMailbox{1f05a927-8a09-492d-ae8f-b4d0de00d60a}
Microsoft Exchange Federation Mailbox FederatedEmail.4c1f4d8b-8179-4148-93bf-00a95fa1e042
Microsoft Exchange SystemMailbox{e0dc1c29-89c3-4034-b678-e6c29d823ed9}
E4E Encryption Store - Active SystemMailbox{D0E409A0-AF9B-4720-92FE-AAC869B0D201}
Microsoft Exchange SystemMailbox{2CE34405-31BE-455D-89D7-A7C7DA7A0DAA}
Microsoft Exchange Migration Migration.8f3e7716-2011-43e4-96b1-aba62d229136
SystemMailbox{8cc370d3-822a-4ab8-a926-bb94bd0641a9} SystemMailbox{8cc370d3-822a-4ab8-a926-bb94bd0641a9}
Note: There's also one type of system mailboxes for monitoring. These should not be moved. They are created automatically and removed when the database is deleted. We display them with Get-Mailbox -Monitoring.
List All Arbitration Mailboxes
Get-Mailbox -Arbitration | FT DisplayName, Name, ServerName, Database -AutoSize
List All Audit Log Mailboxes
A special system mailbox is AuditLog, which we display using a different parameter.
Get-Mailbox -AuditLog | FT DisplayName, Name, ServerName, Database -AutoSize
Moving Migration Mailbox
First we should move the Migration Mailbox.
New-MoveRequest Migration.8f3e7716-2011-43e4-96b1-aba62d229136 -TargetDatabase DBPraha1
Moving All Others
We continue with other Arbitration Mailboxes, we can select them for example by database (if they're in the same one), and Audit Log Mailbox.
Get-Mailbox -Arbitration -Database DB-Praha1 | New-MoveRequest -TargetDatabase DBPraha1 Get-Mailbox -AuditLog | New-MoveRequest -TargetDatabase DBPraha1
List Discovery Search Mailbox
Another special mailbox is Discovery Search Mailbox, which is used to store copies of In-Place eDiscovery search results. It should be automatically created when installing the first server in the organization. There are discussions whether it's needed and should be moved. The safe approach is to move it to the new database.
Get-Mailbox -RecipientTypeDetails DiscoveryMailbox
Moving Discovery Search Mailbox
New-MoveRequest DiscoverySearchMailbox* -TargetDatabase DBPraha1
List Information and Statistics About Move Requests
We can list information about move requests
Get-MoveRequest
Or their statistics
Get-MoveRequest | Get-MoveRequestStatistics
Remove Completed Move Requests
Get-MoveRequest -MoveStatus Completed | Remove-MoveRequest -Confirm:$false
Moving User Mailboxes
The main part is moving user mailboxes. We can specify moving all mailboxes at once, but it's better to divide into smaller parts (even though Exchange has a default limit of 10 concurrent mailbox moves and other moves are paused).
We can use EAC, where we simply define parameters and then can monitor and control progress in the web interface. Here we'll show using EMS, which offers more options. In both cases we can download a report (log) about the mailbox move for individual users (mailboxes).
Note: When moving mailboxes we must constantly monitor sufficient free space for transaction logs.
Number of Mailboxes in Database
Get-Mailbox -resultsize unlimited | Group-Object -Property Database | Sort-Object Name | FT Name, Count -AutoSize
Size of Individual Databases
Get-MailboxDatabase -Status | Sort-Object Name | FT Name, DatabaseSize, AvailableNewMailboxSpace -AutoSize
List of Mailboxes and Their Sizes in Given Database
Get-MailboxStatistics -Database DB-Praha1 | FT DisplayName, Database, ServerName, TotalItemSize, TotalDeletedItemSize, DisconnectDate -AutoSize
Note: The Get-MailboxStatistics cmdlet displays all types of mailboxes, including Disconnected mailboxes (deleted or moved Soft-deleted). Therefore the following output is often useful.
Get-Mailbox -Database DB-Praha1 | Get-MailboxStatistics | FT DisplayName, Database, ServerName, TotalItemSize, TotalDeletedItemSize -AutoSize
List First 20 Mailboxes from Given Database
Get-Mailbox -resultsize unlimited -Database DB-Praha1 | Select-Object -First 20 | FT Name, ServerName, Database -AutoSize
If we want to also see mailbox sizes
Get-Mailbox -resultsize unlimited -Database DB-Praha1 | Select-Object -First 20 | Get-MailboxStatistics | FT DisplayName, Database, TotalItemSize -AutoSize
List Mailboxes Smaller Than 100 MB
Get-Mailbox -Database DB-Praha1 -resultsize unlimited | Get-MailboxStatistics | Where-Object { $_.TotalItemSize -lt "100MB" } |
FT DisplayName, TotalItemSize, TotalDeletedItemSize -AutoSize
Create CSV with Emails of Mailboxes Smaller Than 100 MB
$user = Get-Mailbox -Database DB-Praha1 -resultsize unlimited | Get-MailboxStatistics | Where-Object {$_.TotalItemSize -lt "100MB"}
"EmailAddress" | Out-File d:\users.csv
$user | ForEach-Object { (Get-Mailbox -Identity $_.DisplayName).PrimarySmtpAddress.address } | Out-File d:\users.csv -Append
Move First 20 Mailboxes from Given Database Using Move Request
Primary example of moving a specific number of mailboxes. We can also move all mailboxes from a specific database or server.
Get-Mailbox -Database DB-Praha1 | Select-Object -First 20 | New-MoveRequest -TargetDatabase DBPraha1
Move Mailboxes from CSV Using Migration Batch
New-MigrationBatch -Local -Name LocalMove -CSVData ([System.IO.File]::ReadAllBytes("D:\users.csv")) -TargetDatabases DBPraha1 `
-AutoStart -AutoComplete
Information and Statistics About Move Requests
Get-MoveRequest | Get-MoveRequestStatistics | FT -AutoSize
Display History of Completed Moves for Mailbox
Get-MailboxStatistics -Identity bouska -IncludeMoveHistory | FL DisplayName, MoveHistory
More detailed display
(Get-MailboxStatistics -Identity bouska -IncludeMoveHistory).MoveHistory
Report (Log) About Mailbox Move
The history of completed moves in the mailbox also contains a detailed report (log) of the move. We can list it for all moves.
(Get-MailboxStatistics -Identity bouska -IncludeMoveReport).MoveHistory | FL Report
Only for the latest
(Get-MailboxStatistics -Identity bouska -IncludeMoveReport).MoveHistory[0] | FL Report
For existing Move Request we can also use another cmdlet.
Get-MoveRequestStatistics -Identity bouska -IncludeReport | FL Report
Optionally save output to CSV using | Export-CSV d:\report.txt
Remove Completed Requests
Get-MoveRequest -MoveStatus Completed | Remove-MoveRequest -Confirm:$false
Delete Mailbox Content
If we needed to delete entire mailbox content before moving (for example some service mailbox), we can use the Search-Mailbox cmdlet. We need the Mailbox Import Export role.
Search-Mailbox bouska -DeleteContent
Alternatively we can remove only deleted items (which are normally kept for 14 days after deletion).
Search-Mailbox bouska -SearchDumpsterOnly -DeleteContent
Public Folders (PF)
- Exchange Server 2016 Public Folders and their migration - my older article
- Public folders in Exchange Server
Since Exchange 2013, public folders use a special mailbox (Public Folder Mailbox) inside a standard Mailbox Database. The hierarchy and content of public folders are stored in the mailbox. Public folder migration consists of a classic move of their mailbox.
Structure and Nesting
- Mailbox Database - we can have a dedicated database (one or more) only for PF mailboxes or shared with regular recipient mailboxes
- Public Folder Mailbox (PF Mailbox) - inside the database we can create one or more mailboxes for PF
- Public Folder (PF) - inside each PF mailbox we can create a number of public folders
When creating a public folder we cannot specify the PF mailbox where it should be placed. PF Mailbox can have a maximum size of 100 GB and 2000 concurrent user logins. To move public folders to another mailbox we can use scripts Split-PublicFolderMailbox.ps1 and Move-PublicFolderBranch.ps1 or the New-PublicFolderMoveRequest cmdlet.
Public Folder Quotas
PF Mailbox is located in a regular Mailbox Database, so by default it inherits mailbox size limits (IssueWarningQuota, ProhibitSendQuota, ProhibitSendReceiveQuota) from the database settings. Commonly PF mailboxes are used much larger than user mailboxes, so we must adjust the settings (on database or mailbox).
These settings apply to the entire mailbox, and therefore together all public folders located in it. We can also set limits on individual public folders, which applies only to the given folder (content of subfolders is not counted). We set this using Set-PublicFolder, default setting is unlimited.
We must monitor the public folder mailbox size, and if it fills up too much, move some PF to another (new) mailbox or enlarge it. This also happened to me in practice. Suddenly mail forwarding rules from PF stopped working. It took me time to figure out that the mailbox had filled up considerably and the Prohibit Send limit was applied. But it was good that it was before Prohibit Send Receive was applied.
Moving Public Folders
We perform regular mailbox moves, but must use EMS. Within EAC - Migration, public folder mailboxes are not offered.
Number of PF Mailboxes in Database
Get-Mailbox -PublicFolder -resultsize unlimited | Group-Object -Property Database | Sort-Object Name | FT Name, Count -AutoSize
List of PF Mailboxes and Their Sizes
Get-Mailbox -PublicFolder | Get-MailboxStatistics | FT DisplayName, Database, ServerName, TotalItemSize, TotalDeletedItemSize -AutoSize
List Public Folders Larger Than 512 MB (Nesting Not Counted)
Get-PublicFolderStatistics -ResultSize Unlimited | Sort TotalItemSize -Descending | where { $_.TotalItemSize -gt 524288000 } |
FT Name, FolderPath, ItemCount, TotalItemSize, MailboxOwnerId -AutoSize
Move One PF Mailbox
We usually don't have that many public folder mailboxes, so it's possible to move them one by one. Two examples that do the same thing.
New-MoveRequest PFmailbox1 -TargetDatabase DBPF1 Get-Mailbox -PublicFolder -Identity PFmailbox1 | New-MoveRequest -TargetDatabase DBPF1
Move All PF Mailboxes on Given Server
Get-Mailbox -PublicFolder -Server MAILPRAHA | New-MoveRequest -TargetDatabase DBPF1
Information and Statistics About Move Requests
Get-MoveRequest | Get-MoveRequestStatistics | FT -AutoSize
Remove Completed Requests
Get-MoveRequest -MoveStatus Completed | Remove-MoveRequest -Confirm:$false
Removing Mailbox Database in DAG
If the database has a copy on another server (uses DAG), we must first remove all copies before we can delete the active database.
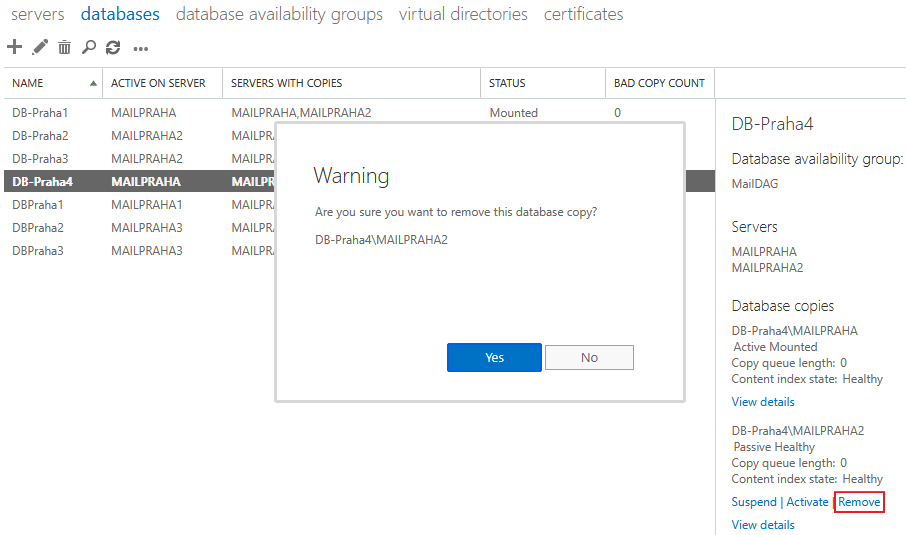
Removing Database Copy
- EAC - Exchange Admin Center
- Servers - Databases
- select the database, on the right in details find the passive copy (must be in Healthy state) and click Remove
- confirm copy removal by clicking Yes and removal information by clicking OK
- manually delete files (database and transaction logs) on the disk of the server where the copy was
Using Exchange Management Shell (EMS):
Remove-MailboxDatabaseCopy -Identity DB-Praha1\MAILPRAHA2
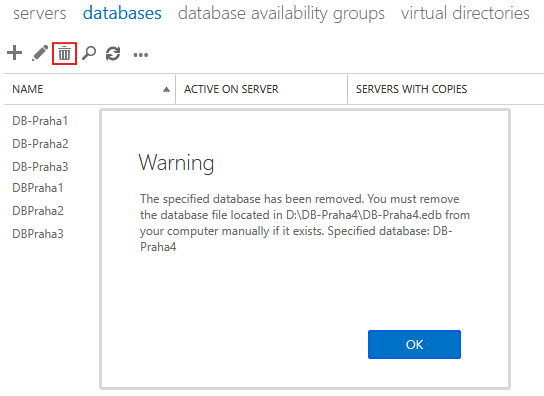
Removing Database
A database can only be deleted when it's empty. With the exception of Monitoring/Health Mailboxes, which are automatically removed when the database is deleted. Therefore it must not contain any user, archive, public folder, arbitration or audit mailboxes.
- EAC - Exchange Admin Center
- Servers - Databases
- select the database and click the trash can (Delete)
- confirm database removal by clicking Yes and removal information by clicking OK
- manually delete files (database and transaction logs) on the server disk
Using Exchange Management Shell (EMS):
Remove-MailboxDatabase -Identity DB-Praha1
There are no comments yet.