Note: I practically installed Exchange Server SE role Mailbox server on Windows Server 2025. In an environment with different internal and public DNS domains and Split DNS (Split-Brain DNS). Into an existing Exchange 2016 organization.
Communication Redirection
Internal communication usually goes directly to the IP addresses of Exchange servers according to DNS records. External communication typically passes through the edge Firewall and uses one public IP address. We have already configured part of the communications, now we need to move (and verify) all communications to the new servers.
Client Access
We addressed Client Access configuration in the second part. For both external and internal access, we used a common URL address (DNS record / Shared namespace). Initially, everything was routed to the original servers. Now we need to redirect to the new servers.
We can either modify the Firewall policies for external communication and change the internal DNS records so that the virtual name contains the IP addresses of the new servers. Or we can change the server IP addresses. We set some new addresses for the original servers. And we change the addresses of the new servers to the original ones. Then communication automatically routes to the new servers. Even in cases where we use the server's IP address for sending mail in some applications.
IP Address Change
The address can be changed simply. For greater certainty, it's possible to switch the new server to Maintenance Mode, change the IP address, and restart the server. Exchange primarily uses DNS names. After changing the address, the server registers a new DNS record. On all other Exchange servers, it's necessary to clear the DNS cache so that servers immediately start using the new address and everything works (for example, DAG).
ipconfig /flushdns
Mail Flow
In the third part, we addressed connector configuration and Mail Flow. We'll resolve incoming SMTP communication by changing server IP addresses or modifying routing on the Firewall and in internal applications. We'll configure outgoing SMTP communication by modifying send connectors, where we change the servers in Source server. We must also properly configure the Firewall so that outgoing and incoming SMTP communication works.
Exchange Hybrid
If we're using Exchange Hybrid, we need to update the configuration. We can display the current configuration using the Get-HybridConfiguration cmdlet.
We install the latest version of Hybrid Configuration Wizard on the new server. We can do this from Exchange Admin Center (EAC) - Hybrid, where there's a link https://aka.ms/HybridWizard. We go through the wizard, where the new Exchange is detected as the optimal server. Other values remain preset. We change the servers in Receive Connector Configuration and Send Connector Configuration and run the update.
We can also address Deploy dedicated Exchange hybrid app.
Removing the Original DAG
In the fourth part, we moved all mailboxes and removed old databases. Now we remove server membership from the original DAG and then delete it.
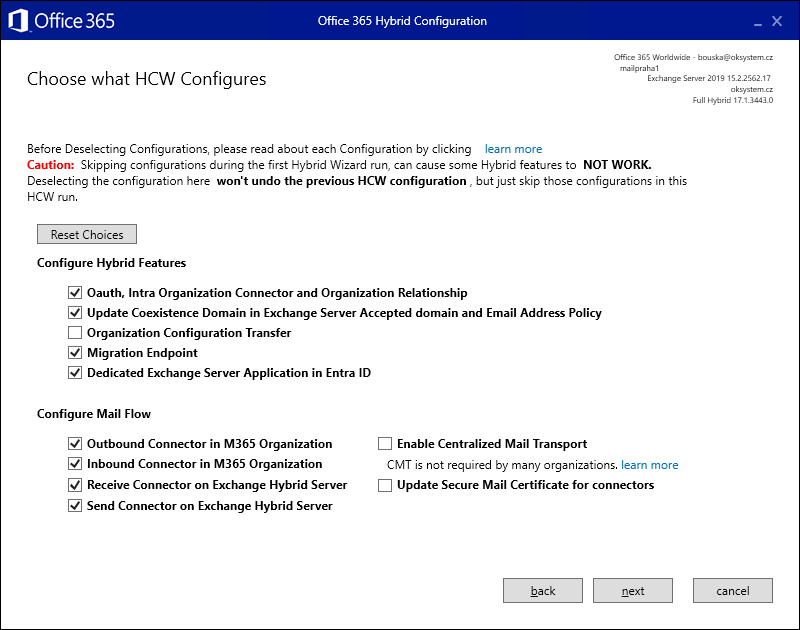
Removing Server Membership from DAG
If the DAG has Datacenter Activation Mode enabled, we must first disable it. This is because it requires the DAG to have at least two member servers.
Checking Datacenter Activation Mode Settings
[PS] D:\>Get-DatabaseAvailabilityGroup | FT Name, DatacenterActivationMode Name DatacenterActivationMode ---- ------------------------ MailDAG DagOnly ExchangeDAG Off
Disabling Datacenter Activation Mode
Set-DatabaseAvailabilityGroup -Identity MailDAG -DatacenterActivationMode Off
Removing DAG Membership
- EAC - Exchange Admin Center
- Servers - Database Availability Groups
- select our DAG and click on the computer icon with a gear (Manage DAG membership)
- select the server and click the minus (Remove), save with the Save button
Removing the DAG
We probably use a DAG with File Share Witness. In the DAG configuration, we find out which folder on which server it is, and then we can remove it.
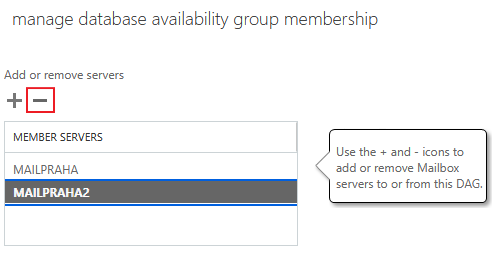
Deleting Database Availability Group
- EAC - Exchange Admin Center
- Servers - Database Availability Groups
- select our DAG and click the trash icon (Delete)
- confirm with the Yes button
Checks and Tests
Incoming and Outgoing Connections
We can check whether connections are still coming to the original servers. In the IIS log we can see client access (MAPI/HTTP, ActiveSync, EWS, OAB etc). In the protocol log (and Message Tracking Logs), whether SMTP traffic is coming or going.
Maintenance Mode
We can switch the original servers to Maintenance Mode for some time and monitor all unexpected problems. Before we perform the Exchange uninstallation.
Remote Connectivity Analyzer
We can verify that all services are working and whether connections are to the new servers. For functionality checks, we can use the Microsoft Remote Connectivity Analyzer.
Exchange Uninstallation
We have completed the migration, so finally we want to decommission Exchange 2016 from our organization. On the original Exchange servers, we perform Exchange uninstallation.
Exchange uninstallation is a similar process to cumulative update installation. Microsoft recommends restarting the server before and after running Setup and turning off antivirus.
Graphical Wizard
We can run the standard Windows application uninstallation using Control Panel - Programs and Features or Settings - Apps - Installed apps / Settings - System - Apps & features. We select Microsoft Exchange Server 2016 Cumulative Update 23 and Uninstall. In some articles, this method is not recommended, but running Setup.exe is preferred.
Command Line
Or we can use the command line (a little tip, we must not change the size of the window during the process, otherwise it will end with an exception) and Unattended Setup. The installation file is located in the path C:\Program Files\Microsoft\Exchange Server\V15\Bin, which we have by default in the PATH variable.
Setup.exe /mode:Uninstall
The uninstallation log is written (just like during installation) to C:\ExchangeSetupLogs\ExchangeSetup.log. The entire uninstallation process in the command line:
C:\>Setup.exe /mode:Uninstall Microsoft Exchange Server 2016 Cumulative Update 23 Unattended Setup Mailbox role: Mailbox service Mailbox role: Unified Messaging service Mailbox role: Client Access service Mailbox role: Transport service Mailbox role: Front End Transport service Mailbox role: Client Access Front End service Management tools Languages Performing Microsoft Exchange Server Prerequisite Check Configuring Prerequisites COMPLETED Prerequisite Analysis COMPLETED Configuring Microsoft Exchange Server Preparing Setup COMPLETED Mailbox role: Mailbox service COMPLETED Mailbox role: Unified Messaging service COMPLETED Mailbox role: Client Access service COMPLETED Mailbox role: Transport service COMPLETED Mailbox role: Front End Transport service COMPLETED Mailbox role: Client Access Front End service COMPLETED Exchange Management Tools COMPLETED Language Files COMPLETED Stopping Services COMPLETED Removing Exchange Files COMPLETED Restoring Services COMPLETED Finalizing Setup COMPLETED The Exchange Server setup operation completed successfully.
Step 8 Languages - Access Denied Error
On one server, I encountered an error during Exchange uninstallation. In step 8, when Language Packs were being removed, the wizard ended with the following error.
Error:
The following error was generated when "$error.Clear();
$regPath='HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall';
$PackageGUIDRegEx = "{9BBCB5[0-9a-fA-F]{2}-AAC3-4BF5-[0-9a-fA-F]{4}-A4D51A19BF14}";
$InstallPath = (Get-ItemProperty 'HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\ExchangeServer\v15\setup').MsiInstallPath;
if(test-path ($regPath))
{
Write-ExchangeSetupLog -info ("Removing " + $RoleLanguagePackType + " Language Packs.");
Get-ChildItem ($regPath) | foreach{
if($_ -match "(?<ProductCode>$PackageGUIDRegEx)") {
$langPackPackageCode = $matches['ProductCode'];
if($langPackPackageCode -ne $null -and $langPackPackageCode.Length -ne 0) {
Write-ExchangeSetupLog -info ("Removing package $langPackPackageCode");
$language = $langPackPackageCode.Substring(20,4);
$logFilePath = [IO.Path]::Combine($RoleLogFilePath,"Uninstall") + '.' + $language + '.' + "OwaPlus" + "." + $RoleLogDateTime + ".msilog";
uninstall-MsiPackage -ProductCode ($langPackPackageCode) -LogFile ($logFilePath);
};
};
};
Get-Childitem -Path $InstallPath -include "*.Localized.js","*.Localized.min.js" -recurse | foreach ($_) {remove-item $_.fullname};
Write-ExchangeSetupLog -info "Remove Language Packs completed.";
};
" was run: "System.UnauthorizedAccessException: Access is denied ---> System.ComponentModel.Win32Exception: Access is denied
--- End of inner exception stack trace ---
at System.Management.Automation.Utils.NativeDirectoryExists(String path)
at System.Management.Automation.SessionStateInternal.IsItemContainer(CmdletProvider providerInstance, String path, CmdletProviderContext context)".
I restarted the server and ran uninstallation from the command line. Everything went through.
C:\>Setup.exe /mode:Uninstall Microsoft Exchange Server 2016 Cumulative Update 23 Unattended Setup Mailbox role: Mailbox service Mailbox role: Unified Messaging service Mailbox role: Client Access service Mailbox role: Transport service Mailbox role: Front End Transport service Mailbox role: Client Access Front End service Languages Performing Microsoft Exchange Server Prerequisite Check Configuring Prerequisites COMPLETED Configuring Microsoft Exchange Server Preparing Setup COMPLETED Language Files COMPLETED Stopping Services COMPLETED Removing Exchange Files COMPLETED Restoring Services COMPLETED Finalizing Setup COMPLETED The Exchange Server setup operation completed successfully.
Conclusion
At the very end, we can perform additional checks and cleanup. Everything depends on our environment.
- remove original servers from backup
- we can verify that the original server accounts were removed from groups in AD
- we can verify that the original servers were removed from the Exchange organization configuration (this also removes its Autodiscover SCP) - using ADSI Edit in the path Configuration - Services - Microsoft Exchange - organization - Administrative Groups - Exchange Administrative Group (FYDIBOHF23SPDLT) - Servers.
- delete the original servers from Active Directory and delete the VM
There are no comments yet.