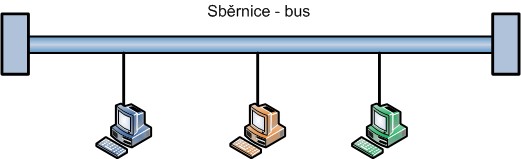
Bus
Bus was used in the early days of Ethernet and was implemented using coaxial cable and BNC connectors, with a terminator always required at the end. All devices are connected to a common bus. This technology has been phased out in networks, and today star topology is predominantly used.
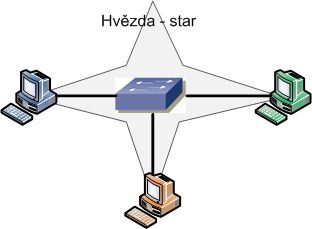
Star - Hub and Spoke
Star is the most commonly used topology for Ethernet today. There is a central element that connects the devices, and individual devices are connected to it. The central element can be a hub or switch, but from another perspective, it can also be a router.
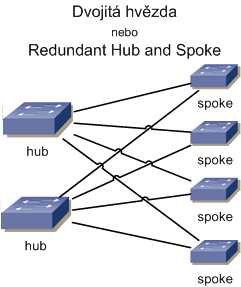
Similarly, there is the Extended Star Topology, which is created when several independent stars are interconnected through central elements. In practice, a three-layer topology (or two-layer, omitting one layer) using star connections is often used today. In the highest layer, there is one or two (for redundancy) switches, called the core. The second layer contains several switches connected to the core, called distribution. The last layer, connected to the distribution, is the access layer, where stations and servers are connected. Some important servers can be connected directly to the distribution layer. The connection where the central element is duplicated is also referred to as a Double Star.
The star topology is also referred to as the Hub and Spoke connection. Here, the term hub is not used as an active network element but is derived from the term for a wheel, where we have a hub and spokes. This term is also used in routing or VPN, where Hub is the central element and Spoke are the branches.
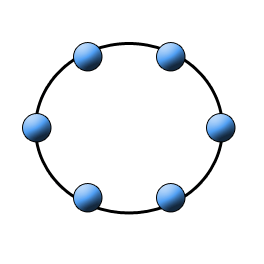
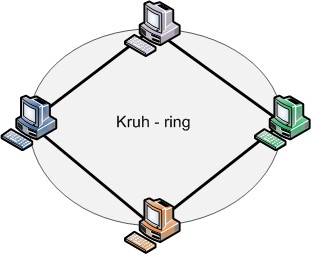
Ring
In a ring topology, each node is connected to two neighbors, forming a ring. Typically, there is only one path between two nodes. An extension is that communication occurs in both clockwise and counterclockwise directions. It is used for FDDI and Token Ring network technologies.
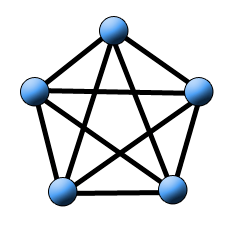
Mesh
In a mesh topology, nodes are connected to multiple neighbors. It can be a Full Mesh, where each node is connected to all others, allowing direct communication with each and easy pathfinding in case of a link failure. However, with more nodes, it becomes complex and expensive. Or it can be a Partial Mesh, where some nodes are directly connected (point-to-point) to multiple other nodes.
A logical Full Mesh is used, for example, for routing with the BGP protocol. Additionally, mesh topology is used in some WiFi networks.
Zdravim Peťo ... hnedle rozesílám link na tvoje stránky všude po světě ... Y36PSI(počítačové sítě) zlobí studenstvo FEL a tohle je dobrej studijní materiál ;)
[4] Čauky, vede ke mě několik odkazů z http://stm-wiki.cz/index.php/Y36PSI, ale já se tam nedostanu. Zajímalo by mě co se tam píše ... ;-)
Jenom poznámčička... možná melu blboviny, ale neni náhodou v jednom obrázku chybička? Na obrázku 000540.jpg je znázorněná topologie Hvězda a máš tam napsáno Hvězda-ring. Třeba se pletu, ale nemá tam být star ?
[6] Jo jo, má tam bejt Hvězda - star, to je tak, když člověk upravuje pořád ten samej obrázek :-)
dobrý stránky.
Zdravím, postrádám tu topologii Strom (TREE)..
[9] V praxi se topologie stromu nepoužívá (pokud vím), protože se používá rozšířená topologie hvězda, což je v důsledku strom.
Chtěl bych se zeptat tebe jako zkušenějšího. A co topologie Mesh (polygoní topologie)? Neměla by tu být taky? Jestli vůbec stojí za zmínku
[12] Samozřejmě topologie Mesh je také možné zapojení sítě. Používá se například ve speciálních WiFi sítích nebo se vytváří virtuální Mesh kvůli routování. Já jsem zde ale uváděl pouze ty nejzákladnější a nejpoužívanější topologie. Existují ještě další (a ještě méně používané).
Zajimalo by me jaky mechanismus se pouziva pri dvojite hvezde pri pripojeni serveru zda to je STP protokol a nektera z jeho podvariant ve spojeni s VRRP nebo LACP na serveru, nebo zda existuje nejake jine reseni?