Managed Hardened Repository
Veeam Hardened Repository
Linux Hardened Repository is a special type of backup storage in Veeam Backup & Replication that supports immutability. This storage appeared in Veeam Backup & Replication 11 and was significantly improved in version 12. It supports general Linux servers, so it's possible to choose hardware (physical server with local disks) and Linux distribution according to your needs.
Veeam Hardened Repository ISO
- [RELEASE] Managed Hardened Repository ISO by Veeam
- VBR 12 - Preparing Hardened Repository Using Veeam ISO
In the second half of 2024, Veeam introduced a managed Veeam Hardened Repository that is installed from a prepared VHR ISO. The first public version 0.1.15 was a Community Preview, version 0.1.17 received experimental support. At the beginning of 2025, the latest version VHR ISO 2.0.0.8 was released, still with experimental support.
The Veeam installation is built on the Rocky Linux operating system. The system is hardened according to DISA STIG and automatically updated by Veeam. It uses the XFS file system, which supports Fast Clone (Block Cloning - reflink) and Immutability. It allows deploying secure storage without knowledge of Linux OS.
Veeam Infrastructure Appliance 13
Very shortly before the publication of this article, Veeam Software Appliance 13 (containing VBR 13.0.0) was released. Along with Veeam Infrastructure Appliance 13, which can be used as a Hardened Repository (can only be added to VBR 13). This is the official recommended version intended for future installations of managed Veeam Hardened Repository.
This is still an Early Release and upgrade or migration from VBR 12 is not available. With version VBR 13.0.1, Windows installation should come, the possibility to upgrade from V12, and also the possibility to convert Hardened Repository installed from VBR ISO 2.0 to Veeam Infrastructure Appliance 13.
Veeam Appliance uses Veeam JeOS (Just Enough Operating System). It's a minimalist Linux distribution that is managed by Veeam. It's delivered as a bootable ISO and is pre-hardened according to security best practices. It's built on Rocky Linux. It's an evolution of VHR ISO.
Comparison of VHR ISO 2.0 and JeOS 13.0
The operating principle of Hardened Repository, achieving immutability, and the technologies used remain the same, whether we install from VHR ISO 2.0 or use the new Veeam Infrastructure Appliance 13. The difference is in improved management, configuration, and installation. Newly available is the Veeam Host Management web interface, which allows managing the Appliance through a browser.
A security innovation is Certificate-based authentication when adding a managed server to the backup infrastructure. The Appliance has pre-installed Veeam components (Veeam Deployment Kit), which are used for connection from the VBR server. We don't need to enable SSH access or create single-use credentials. Authentication is performed using certificates. When users log in to the Appliance, Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is used.
Server for Hardened Repository
For secure operation, we need a physical server with local disks. Generally, it can be any hardware with sufficient performance and disk space, but it should be on the Red Hat compatibility list. We can also look at the Veeam Ready program for tested solutions for Hardened Repository.

The server must be sufficiently secured so that an attacker cannot get to the lower layer. If they got into the system as root, they could cancel immutability. If they got to disk management (for example through HPE iLO or Dell DRAC), they could delete them.
Properties of Managed Hardened Repository
- operating system - Rocky Linux, hardened according to DISA STIG, managed/updated by Veeam
- Immutability - based on the XFS file system and use of the Immutable flag attribute
- data transfer between Veeam Proxy and storage occurs over TLS 1.3 within the proprietary Veeam protocol through one TCP/IP port on the Veeam Data Mover
- we can use Veeam deduplication, compression, and encryption
- data is stored on block storage, must be local disks or DAS, condition is HW RAID controller with write-back cache, RAID 6/60 is recommended for data, one disk is used for the system (RAID 1), LVM volume is created from the rest
- built-in system time change detection (time drift)
- uses Forward Incremental Backup Chain
- uses single-use credentials that are not stored in Veeam configuration, Veeam Infrastructure Appliance 13 uses Certificate-based authentication (and pre-installed Veeam components)
- disabled SSH access and we don't have access to the
rootaccount - support for Fast Clone, saves space and time when creating synthetic full backups
- we must properly secure remote access to HPE iLO, Intel BMC, etc., because through this remote management (IPMI) it's possible to destroy data on the disk
How Immutability Works on Hardened Repository
- Veeam Backup & Replication - Immutable Repositories and Secure Backups
- Understanding Immutable Backups and Their Role in Cyber Resilience
- Protect against Ransomware with Immutable Backups
- VBR 12 How Immutability Works
- VBR 13 How Immutability Works
Immutability
Immutability ensures that data (backups) cannot be changed or deleted for a specified time (Immutability Period) after their creation. It's the principle of Write Once Read Many (WORM), where we can write data once and read it unlimited times. Thanks to Immutable Backups, we ensure security, integrity, and compliance of backed-up data.
In Veeam Hardened Repository, immutability is set at the operating system level using file system properties.
Backup Repository
Immutability is set for the entire Repository in its properties. It's therefore the same for all backup jobs that store backups on the given Repository. We specify the number of days for the immutability period, minimum is 7 days.
Retention Policy
Each successful run of a backup job (backup execution) creates a Restore Point. For the backup job, we set a Retention Policy that determines how long backups are retained. At least 3 Restore Points are always retained.
It's recommended to set the Immutability Period shorter than or equal to the Retention Policy. If Immutability is longer, files won't be deleted when Retention expires, but only when they are no longer protected by immutability.
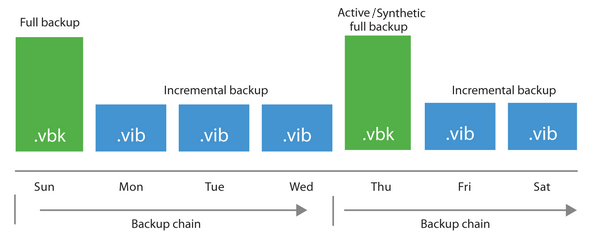
Backup Chain
For Hardened Repository, only Forward Incremental Backup Chain is used (with active or synthetic Full Backup enabled, otherwise it would be Forever Forward Incremental). We cannot use Reverse Incremental. When immutability is set on backup files, they cannot be merged or deleted before its expiration.
Forward Incremental
- first runs active full backup (VBK)
- then incremental backups run (VIB)
- regularly scheduled execution of synthetic or active full backup (VBK), which divides the Backup Chain into shorter series
- after adding a new restore point, the Retention Policy of the given job is checked, if the entire Backup Chain exceeds retention, the whole chain is removed (at least the current chain must remain)
It depends on how often we perform full backup and what the retention is. If we do Full Backup once a week and want to maintain 7 days, it will be kept for 7 to 14 days.
Active Backup Chain and Immutability
Veeam Backup & Replication sets immutability on the entire Backup Chain with all its Restore Points (RP). Backup Chain only makes sense when it's available as a whole (VIB without VBK is unusable). Therefore, with Forward Incremental, some RPs are kept longer than set by retention. Immutability is applied in the same way, so that part of the Backup Chain cannot be deleted and rendered unusable.
The active backup chain has the same immutability date according to the creation of the last restore point. When a new Restore Point is created, Immutability is set according to the period specified on the storage. At the same time, it's automatically extended on all files in the active chain. If an inactive chain exists, immutability is not extended for it.
Immutability is set on files with backed-up data (VBK, VIB, etc.). It's not set on backup metadata file (VBM) because it's updated with each job run. Immutability flag is set on a file when the current backup session is completed. If GFS is used, immutability for full backups with GFS is set as the longest of both periods (often according to GFS).
Veeam Plug-ins for Enterprise Applications
A special case is backing up using Veeam Plug-ins (Enterprise Application Backups), where Immutability behaves a little differently. For example, backing up Oracle Database using Veeam Plug-in for Oracle RMAN.
- similarly, immutability is set on VAB and VASM files, not VACM
- Immutability is set only after 24 hours have elapsed from the file creation
- the immutability period is not extended for the active backup chain
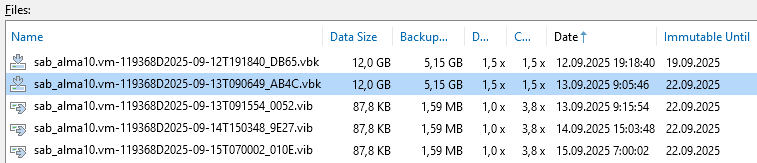
Below is an example of the status as of October 8th at 4 PM. The previous day's backup has immutability set, but today's does not yet.
[veeamsvc@backupstorage ora-cluster.oksystem.local Oracle backup _backupStorage_]$ ls -l -a total 23601748 drwxr-xr-x. 2 veeamsvc veeamsvc 4096 Oct 8 03:46 . drwx------. 11 veeamsvc veeamsvc 4096 Oct 6 12:52 .. -rw-r--r--. 1 veeamsvc veeamsvc 18367512576 Oct 7 03:45 0e0b5488-78c1-4355-b3ea-9e07e2a4f28f.vab -rw-r--r--. 1 veeamsvc veeamsvc 26243 Oct 7 03:45 0e0b5488-78c1-4355-b3ea-9e07e2a4f28f.vasm -rw-r--r--. 1 veeamsvc veeamsvc 5800280064 Oct 8 03:45 cc6a23a7-73ec-44d3-b861-0dbebae5c648.vab -rw-r--r--. 1 veeamsvc veeamsvc 22575 Oct 8 03:46 cc6a23a7-73ec-44d3-b861-0dbebae5c648.vasm -rw-r--r--. 1 veeamsvc veeamsvc 20156 Oct 8 03:46 'ora-cluster.oksystem.local Oracle backup _backupStorage_.vacm' -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 307 Oct 7 13:59 .veeam.1.lock [veeamsvc@backupstorage ora-cluster.oksystem.local Oracle backup _backupStorage_]$ lsattr -a ---------------------- ./. ---------------------- ./.. ----i----------------- ./0e0b5488-78c1-4355-b3ea-9e07e2a4f28f.vab ----i----------------- ./0e0b5488-78c1-4355-b3ea-9e07e2a4f28f.vasm ----i----------------- ./.veeam.1.lock ---------------------- ./cc6a23a7-73ec-44d3-b861-0dbebae5c648.vab ---------------------- ./cc6a23a7-73ec-44d3-b861-0dbebae5c648.vasm ---------------------- ./ora-cluster.oksystem.local Oracle backup _backupStorage_.vacm
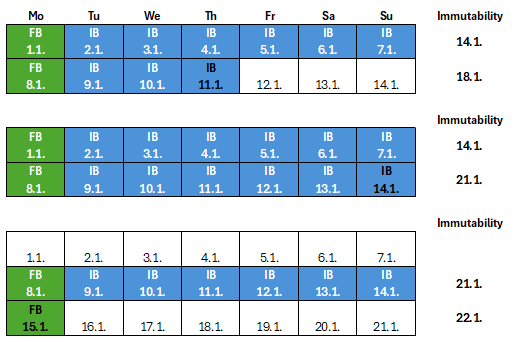
Example of Setting and Extending Immutability
- Retention Policy 7 days
- Full Backup on Monday
- Immutability Period 7 days
The following figure schematically shows existing Restore Points on storage for a specific day (the last one with black text).
- green FB represents Full Backup, initially active, later created by merging the previous full backup (FB) with subsequent incrementals (IB)
- blue IB represents Incremental Backup
- each row always contains one Backup Chain and on the right is the immutability date, which is progressively updated for the active chain
Note: Deletion of older Restore Points (entire Backup Chain that is outside retention) occurs either during backup job execution or through Background Retention.
Changing Immutability Period
If we increase the Immutability Period in the Repository settings, it's applied to the entire active chain on the next job run. If we decrease the value, the original value remains on all existing files and the decreased value is used for new incremental backups.
Extending Immutability for Existing Backup Files
We can use Powershell cmdlet to extend the Immutability date (it cannot be shortened).
Set-VBRImmutabilityLockExpirationDate -RestorePoint $restorePoint -ExpirationDate "2025-12-14 10:00:00Z"
Hardened Repository Server
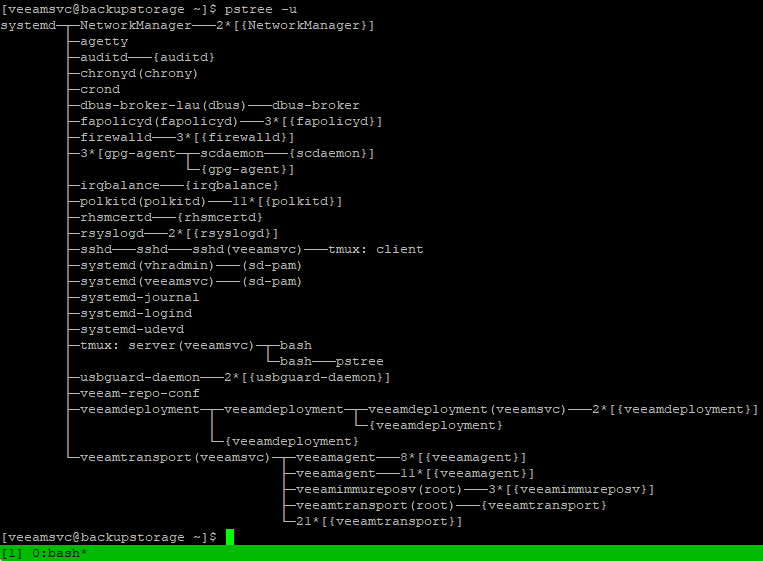
Veeam Services Running on VHR
- Veeam Data Mover - Transport Service (
veeamtransport) - runs as non-root user, communicates with backup server, uses port 6162 - Veeam Immutability Service (
veeamimmureposvc) - runs with root privileges but is local and has no network access, checks immutability attributes every 20 minutes, calculates immutability time for files and sets or removes Immutable attribute, also performs time drift detection - Veeam Installer Service for Linux (
veeamdeploymentsvc) - handles deployment and updates
Veeam Users in the System
Veeam Hardened Repository ISO
vhradmin- account for server management, can only log in through (physical or virtual) console of the server (not via SSH), has access to Veeam Hardened Repository Configuratorveeamsvc- non-root account with selected root-equivalent permissions, password is generated when SSH is enabled, can remotely log into the system (or through console), used by Veeam Backup & Replication for deployment and management of Hardened Repository, Granular sudo Permissions Required for Hardened Repository
Veeam Infrastructure Appliance 13
veeamadmin- account for server management (Host Administrator), can log into Veeam Host Management Console (Web UI or TUI - server console)veeamso- Security Officer account, serves to approve sensitive (destructive) operations, access through Veeam Host Management Console (Web UI)
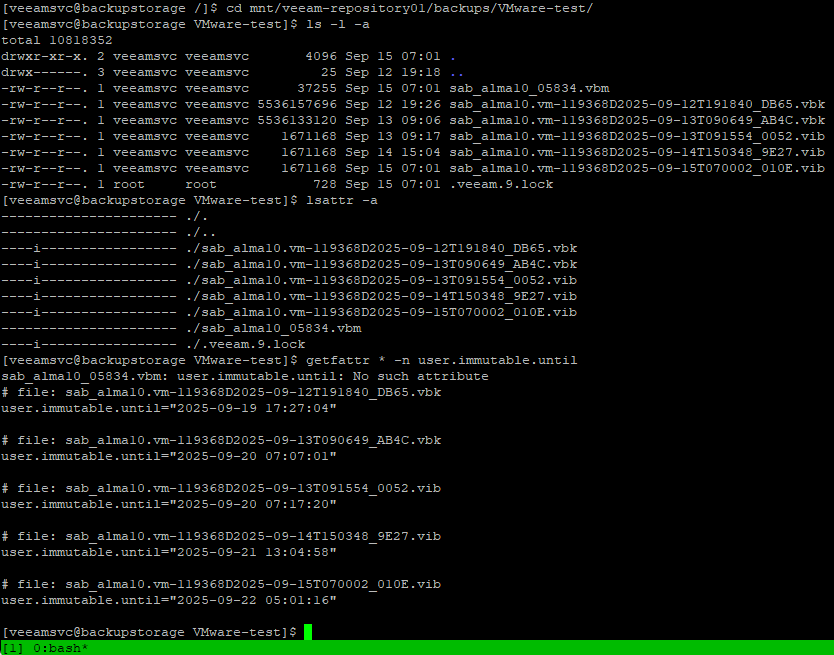
File Attributes for Immutability Control
To ensure immutability, XFS file system properties are used. On backup files the following is set:
- Immutability attribute (flag)
i, we can list it usinglsattr -a, set usingchattr +i - Extended attribute (xattr)
user.immutable.until, metadata with information about the time period of immutability, we can list usinggetfattr * -n user.immutable.untilorgetfattr * -d
Immutability attribute is important. If it's set on a file, we cannot delete it (the file won't be deleted even by the root user, but root can remove the attribute using chattr -i). Immutability Service sets the attribute and removes it after the period expires (both the time period in the user.immutable.until attribute and in the .lock file must end), so the file can then be deleted (for example, through Retention Policy).
.lock File
For each backup job, a .veeam.N.lock file is also created, which contains information about the time period of immutability for individual files. With each backup job run, a new file is created and the old one is deleted. N is a digit that increases each time. The immutability time information is therefore stored twice and Veeam uses information from the .veeam.N.lock file.
When an incremental backup runs, the immutability time increases for all files in the active chain. Data in the .lock file is modified, but the user.immutable.until metadata in the file system doesn't change (the original date remains).
There are no comments yet.