Note: The description in the article is based on Veeam Backup & Replication 11a, licensed using the Veeam Universal License (VUL), which is similar to Enterprise Plus.
Backup Job
In previous parts, we went through the theory and basic functioning of Veeam Backup & Replication (VBR), so now we can create a reasonable backup job with this knowledge. The prerequisite is that we have Veeam Backup & Replication installed and configured, with added components, including data sources for backup.
We can create a backup job from the Home perspective (but practically from anywhere), for example, from the Home tab menu, select Backup Job. Jobs are divided by backup source type and a job can only contain objects of the same type.
We can create a job to back up almost everything that Veeam supports. Typically, this includes
- virtual machines (VM) VMware vSphere (VMware Backup), Microsoft Hyper-V (Hyper-V Backup)
- file shares (File Share Backup)
- Veeam agents with various OS, such as Windows computer (Windows Agent Backup) and Linux computer (Linux Agent Backup)
It is not possible to create a job for backup using Veeam Plug-in (it is created by remote configuration of the plugin).

Virtual Machine (VM) Backup Job
Standard VM backup is done through virtualization, so we do not need network (LAN) access to the VM. This is only needed for Guest Processing, where the backup server connects to the OS over the network. Processing takes place on the Backup Proxy.
When creating or editing a backup job of type Virtual Machine (VMware vSphere and Microsoft Hyper-V are almost identical), we go through the wizard and set various parameters on several tabs. A brief list of most items:
- Name - each job must have a unique name that indicates its purpose/content
- Virtual Machines - the basis of the job is to determine which virtual machines we will back up, we can add VM, VM containers (if a new VM is added to the container, it is automatically added to the backup job) or VM Tags (tags, again automatically added marked VMs)
- in the toolbar (in the upper right corner) we can switch views to see certain objects
- we can also use Exclusions to exclude certain VMs from the backup, VM disks or VM templates
- individual VMs are processed sequentially, we can adjust the preferred order
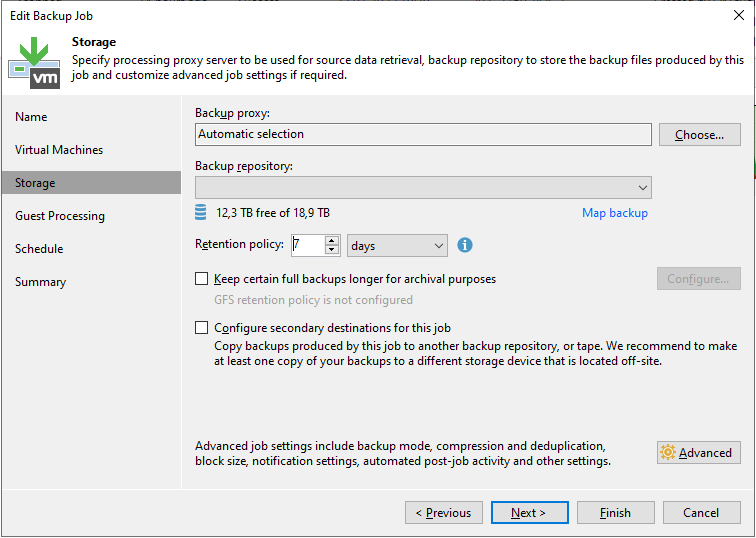
- Storage - we set many important backup properties and backup retention
- Proxy, Repository (using Map backup we can map the job to existing backups), Retention Policy (how many restore points or days we want to keep), GFS (long-term retention policies)
-
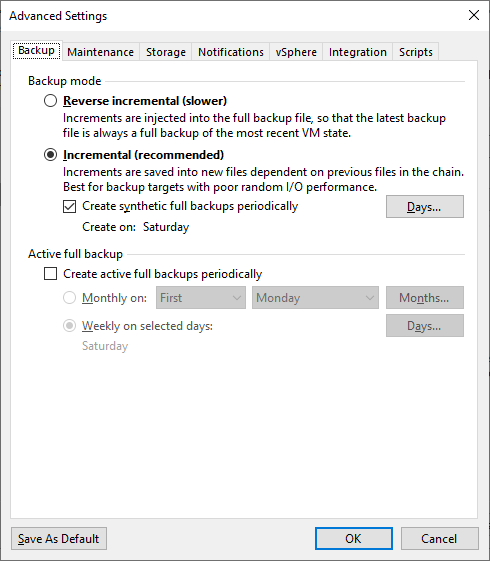
- Advanced - Backup - backup method (Backup mode) and the option to create a Full Backup (Active or Synthetic), if we do not set Full Backup for Incremental, it will be Forever Forward Incremental
-
- Advanced - Maintenance - we can schedule regular maintenance tasks, check the last Restore Point - Perform backup files health check (It is important that there is no conflict with the time when the backup is taking place) and maintain Full Backup, if we do not perform regular active full backups, it involves deleting removed VMs from backups (when the VM was deleted or removed from backup) - Remove deleted items data after, defragmentation and compaction (creates a new full backup, copying data into it) - Defragment and compact full backup file
- Advanced - Storage - setting data reduction - deduplication, compression, excluding Windows swap files and deleted blocks, storage optimization (block size), and encryption of backups
- Advanced - Notifications - setting notifications when the job is completed (we can set it globally or adjust for individual jobs, to set it on a job, it must be enabled globally, for example, if we do not enable global Success, it will not work when set on a job) - SNMP, email, for VMware set VM attribute
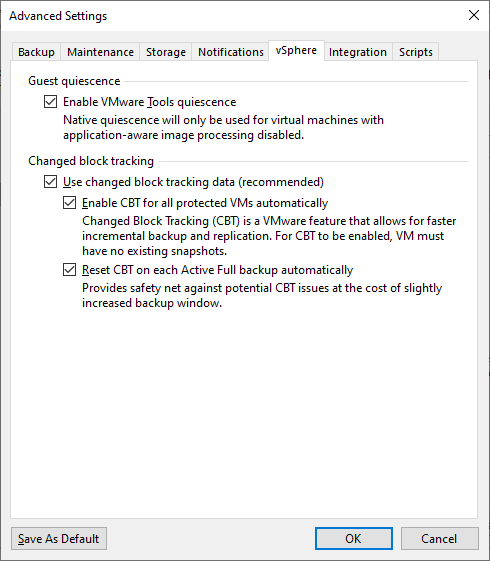
- Advanced - vSphere / Hyper-V - enabling Guest quiescence (calming VMware tools quiescence or Hyper-V guest quiescence) freezes the VM file system (brings it to a consistent state) during backup, Veeam recommends using their own Application-aware Processing instead, and enabling Changed block tracking, for Hyper-V it is recommended to use Allow processing of multiple VMs with a single volume snapshot (does not work for Hyper-V Server 2016 with On-Host Proxy)
- Advanced - Integration - for VMware we can set Backup from Storage Snapshot (enabled by default)
- Advanced - Scripts - we can run custom scripts before and/or after the backup job
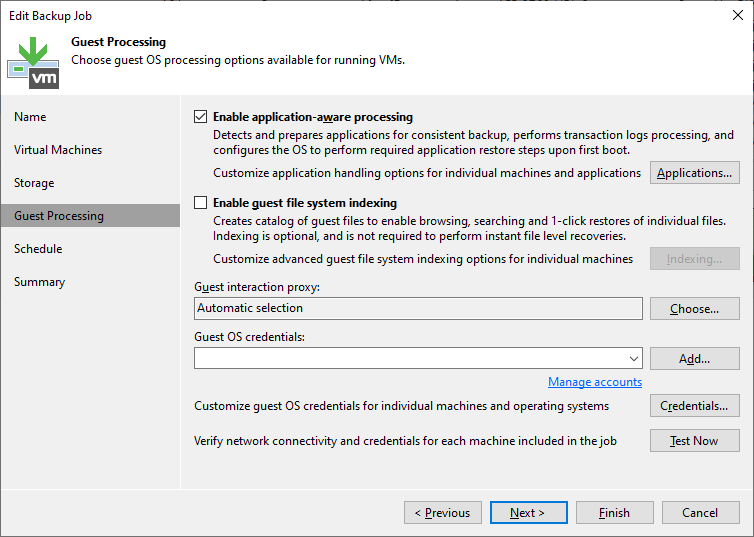
- Guest Processing - we can enable various operations where Veeam communicates with the VM operating system, using either temporary components (Non-Persistent Runtime Components), which are deployed at the start of the job, or (preferably) a persistent agent (Persistent Guest Agent - Guest Helper and Log Shipping Service), which requires fewer open ports
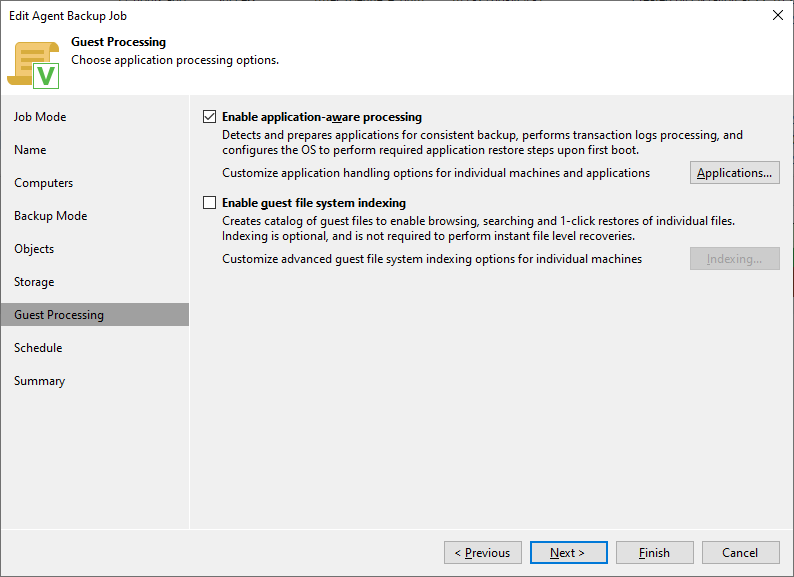
- Application-Aware Processing - detects and prepares applications for consistent backup
- Guest File System Indexing - creates a file catalog that allows browsing, searching, and one-click recovery from Veeam Backup Enterprise Manager, not needed for Instant File Level Recovery
- Schedule - we can schedule regular job runs (the other option is to run manually)
- we can set a specific time daily or monthly, repeat throughout the day or chain jobs, where the job runs after another selected scheduled job is completed (chaining jobs has certain risks, it is recommended to avoid it)
- we can enable automatic retry of failed VM backups
- terminate the job if it exceeds the allowed backup window
Retention Policy
When the specified number of restore points or days is exceeded, the oldest Restore Point is removed. However, for Forward Incremental with Periodic Full Backup, some Restore Points are retained longer than specified. This is because the entire Backup Chain can only be deleted when the last dependent incremental backup is no longer under the Retention Policy. Practically, this means that most of the time we have more Restore Points retained. If, for example, we do a Full Backup once a week and want to keep 7 days, it will be retained for 7 to 14 days.
Guest Quiescence
By default, when backing up a running VM, Veeam Backup & Replication performs a Crash-consistent backup, where VM disk data is read without saving data in memory (does not preserve the integrity of open file data of transactional applications). If we want the file system and application data to be in a consistent state, we can use Guest Quiescence or Application-aware Image Processing.
Quiesce or Freeze the VM, bringing the file system to a consistent state. This helps create transaction-consistent backups. However, to bring an application that does not support Microsoft VSS to a transaction-consistent state, we must use pre-freeze and post-thaw scripts.
Guest Quiescence uses VMware Tools or Hyper-V Integration Services. It allows backing up VMs that do not support Microsoft VSS, such as Linux VMs, where it performs freezing. For Windows VMs, VMware Tools can use the VMware VSS component.
If the backup job includes both Windows and Linux VMs, it is recommended to enable both Guest Quiescence and Application-aware Processing. First, Application-aware Processing is attempted, and for VMs where it fails, Guest Quiescence is used. In the Guest Processing settings for individual VMs, we must select Try application processing, but ignore failures.
Guest Processing
Guest processing options are advanced tasks that require Veeam Backup & Replication to communicate with the guest OS of the running virtual machine (typically over the network, or using VMware VIX API or Microsoft PowerShell Direct on Windows VMs). We must provide credentials with sufficient permissions to log into the OS.
- Application-Aware Processing - allows creating transaction-consistent backups of VMs running Microsoft Active Directory, Microsoft Exchange, Microsoft SharePoint, Microsoft SQL Server, or Oracle Database
- Pre-freeze and post-thaw scripts - we can use scripts before and after freezing for applications that do not support Microsoft VSS
- Transaction log truncation - we can set the truncation of the transaction log after a successful backup, Exchange DAG is supported (logs are truncated when any node is backed up)
- Transaction logs backup for Microsoft SQL Server and Oracle Database - backing up SQL Server transaction logs or Oracle DB archive logs, a parent job is created that backs up the VM, and a child job that regularly backs up the logs, in case of server failure, the VM is restored and transaction logs are applied using Veeam Explorer
- VM guest file system indexing - creates a file catalog that allows browsing, searching, and one-click recovery from Veeam Backup Enterprise Manager, not needed for Instant File Level Recovery
- VM guest OS files exclusion - we can exclude/include certain files or folders from the backup
Application-Aware Processing creates transaction-consistent backups by processing application logs. It uses Microsoft VSS, which brings applications in the VM to a quiescent state. So there are no unfinished database transactions or incomplete files at the moment when the VM Snapshot / Checkpoint is taken. VMware Tools or Hyper-V Integration Services must be installed in the VM.
During VM processing, information about installed applications is gathered, Microsoft VSS brings applications to a quiescent state, a VM VSS snapshot is taken, a VM Snapshot is taken for VMware vSphere or a Volume Snapshot for Hyper-V, Microsoft VSS resumes I/O activities of the guest OS. The backup job continues as usual. Optionally, transaction logs are truncated.

Note: The options available in Guest Processing vary by job type. For VM Hyper-V, VMware, and Windows Agent they are quite similar. Linux Agent has more significant changes. The next article contains screenshots of the different variants.
If there are any errors during Guest Processing within the VM, we can check the Guest Helper log. It is located on the file system inside the VM, for Windows the path is C:\ProgramData\Veeam\Backup\VeeamGuestHelper_19102022.log.
Guest Processing and Access
At the bottom of the Guest Processing step, there is a very useful Test Now button. For all backed-up VMs, it performs connection verification to the VM using various methods (i.e., whether communication is available and login is successful). For Windows VMs, it tests network connection using RPC, further on VMware using VIX, on Hyper-V using PowerShell Direct, and tries access to admin$ share. If we selected Use Persistent Guest Agent, it verifies access to this service.
A log of performed actions and their status is displayed, in case of failure also error information. Not all methods need to be successful for communication to be possible. If we have a Persistent Guest Agent installed, it is primarily used. Otherwise, RPC is used. If it is not network available, VIX/PowerShell Direct is tried. Using the admin share, Non-Persistent Runtime Components (or Persistent Agent Components) are temporarily installed. If we use a persistent agent, this access is not needed.
The agent can be installed manually using the Installer Service (VeeamInstallerSvc.msi, found on the Veeam server in C:\Program Files\Veeam\Backup and Replication\Backup\Packages). More information in Persistent Agent Components.

Some accesses may not pass because they are blocked by User Account Control (UAC). Mentioned in the documentation Persistent Agent Components, more detailed in Local Account with administrative access or Access is Denied. When Using a Local Account to Add a Windows Machine to Veeam Backup & Replication. It talks about a situation where a local (non-domain) account is used for Guest Processing, which may be in the Administrators group. UAC blocks such an account for remote access. If using a local account, it is recommended to use the built-in Administrator account (UAC works differently for it).
I encountered a problem when the Veeam server was not in the domain, but a domain account was used for Guest Processing. Still, access via VIX did not work. Veeam has two articles Troubleshooting Guest Processing Test Now issues and Credentials Test or Job Fails when attempt to use VIX.
An error was displayed, starting with:
Connecting to guest OS via VIX Error: Cannot connect to host [x.x.x.x] over web services. Login: [account-vmware]. Guest Login: [account-windows].
Could not copy host file [C:\Program Files (x86)\Veeam\Backup Transport\GuestInteraction\VSS\VeeamGuestHelpers\VeeamVixProxy.exe] to guest [C:\Windows\TEMP\{409c833b-3225-48d4-9190-13170a21871e}]
I tried disabling UAC on the Veeam server, then the error slightly changed:
Connecting to guest OS via VIX Error: Cannot connect to host [x.x.x.x] over web services. Login: [account-vmware]. Guest Login: [account-windows]. Failed to execute Pwdkey Failed to execute vSphere API command: [Failed to set registry value BiosUUID Failed to create SOFTWARE\VeeaM\Veeam Backup and Replication registry key Win32 error:Access is denied. Code: 5].
I tried disabling UAC on the backed-up VM and subsequently everything went through without error (I haven't investigated further, I don't need VIX).
Disabling UAC in Windows probably isn't enough through the Control Panel, but must be done through the registry. In the path HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System change the value of EnableLUA from 1 to 0. Then a restart is needed. (Best Practice Guide states that in the same place we can create the value LocalAccountTokenFilterPolicy with 1, but that didn't work for me).
Data Exclusion
Veeam Backup & Replication by default backs up the image of the entire VM. However, we have several options to exclude certain data from the backup.
At the VM level
- VM disks - normally all disks are backed up, but we can select only certain IDE, SCSI or SATA disks, for VMware we can have the VMX file modified to exclude non-backed-up disks (and the VM will start), it works very well, which disk it is can be seen in the VM settings or in Windows in Disk Management, typically SCSI is used and gradually 0:0, 0:1, 0:2
- VM templates - for VMware we can choose whether to back up VM templates, or only during a full backup
- VM from VM container - if we back up the entire VM container, we can select certain VMs that should not be backed up
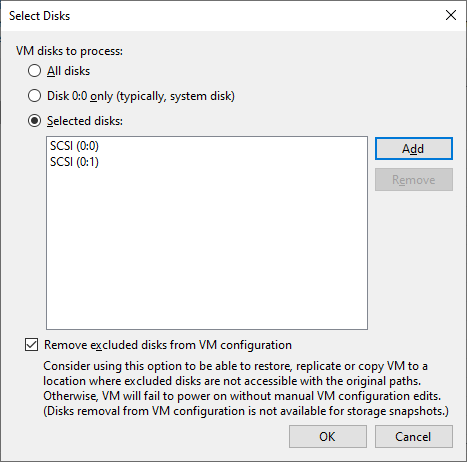
At the VM operating system level
- files and folders - within Guest Processing we can exclude certain files and folders from the backup or, conversely, back up only selected ones, files can be specified using full path, environment variables, or file masks, works only for NTFS, does not support RAID in OS, if we use a mask, the entire disk is searched, which is time-consuming and burdens the VM
- Swap file - by default Exclude swap file blocks is checked and the pagefile.sys and hiberfil.sys files from Windows VM with NTFS are not copied
- Deleted file blocks - by default Exclude deleted file blocks is checked and dirty data blocks (marked as deleted) are not copied, works only for NTFS
Recommendations for Backup Job
Maximum VM per Job
- Veeam recommends using multiple VMs per job (not creating a separate job for each VM), but on the other hand not exceeding a certain amount
- if we have backup files per job, then up to 30 VMs per job
- if we have backup files per VM, then up to 200 VMs per job
Use per-VM backup files
- in many places it is recommended to store each backed-up VM within the job in a separate file (as opposed to one file for the entire job), in VBR 12 this should be the default setting
- the disadvantage is that deduplication between VMs is not performed, so it takes up slightly more space
- Backup Infrastructure - Backup Repositories - right-click Properties - Repository - Advanced - Use per-machine backup files
Repository with Fast Clone
- it is recommended to use Fast Clone, which can save space during synthetic full backup, details Fast Clone
- must be formatted using the ReFS 3.1 or XFS file system
- for Linux Repository with XFS we must enable Fast Clone
- Backup Infrastructure - Backup Repositories - right-click Properties - Repository - Use fast cloning on XFS volumes
- for Microsoft Windows (at least Server 2016 or Windows 10 Pro) it is used by default if conditions are met
Note: A major drawback, in my opinion, is that there are no tools in the system for ReFS that show various statistical data. For example, for a folder, how much data it physically occupies, how much we saved thanks to Block Cloning, etc. We can only display data about the entire disk, how much is occupied and free. Then the size of all folders on the disk, which will usually be more than is occupied. Based on that, we calculate the total space savings. I found only one tool blockstat, which is not very ideal, it compares the stored blocks of specified files and shows how much was saved.
Storage Latency Control
- description Storage Latency Control
- to prevent storage overload where VMs are stored, we can enable latency control, monitoring current load and, at certain values, not starting new jobs or limiting the speed of running ones
Storage Maintenance
If we use the Forever Forward Incremental or Reverse Incremental backup method, it is recommended to enable Defragment and compact full backup file (temporarily requires more storage space). If we do not use Active Full Backup, it is recommended to regularly perform Perform backup files health check (Storage-level corruption guard).
Storage Optimization
In most situations, it is recommended to have deduplication and compression enabled. The default settings should be optimal in terms of backup size and resource usage during the backup (or restore) process. If we store backups on a deduplication appliance, it may be appropriate to set Decompress backup data blocks before storing on the Repository. Still, use compression in the job settings, as it saves data during transfer.
Veeam Agent Backup Job
Agent Installation
We will not focus too much on the installation of the Veeam Agent, which can be done in various ways (much depends on the operating system, the best support is for Windows). The simplest is automatic deployment from the Veeam Server.
We can either create a Protection Group for deploying and managing agents, where the agent can be installed when the group is created (and on newly added computers during Rescan - Agent Discovery). Or add individual computers directly to the Backup Job, the agent is installed at the first run, and the computer is added to the group (Protection Group) Manually Added. During configuration, we must use an account that has installation permissions on the given computers. On Windows, the Changed Block Tracking (CBT) driver can be installed, which allows tracking changes at the block level (not just files). After installation, a system restart is required. The Linux installation includes the Kernel module Veeam Agent for Linux Driver (veeamsnap) for creating Snapshots and CBT.
Agent and Job Modes
The Agent can be standalone (Standalone mode, Veeam Agent for Microsoft Windows), installed directly on the computer. Management is done by the user in the agent or with integration into Veeam Backup & Replication. Or managed (Managed mode, Veeam Agent Management Guide), installed remotely from Veeam Backup & Replication. All operations (management) are performed remotely from the console.
The job can work as managed by the backup server (Managed by backup server), referred to as Backup Job or Veeam Agent backup job managed by the backup server. The backup job runs standardly on the server (as for VM backup), which is suitable for continuously running and connected computers (servers). The agent is lightweight and has no GUI. The agent does not need to be installed from Veeam Backup & Replication, but we can use files generated by it and the group Computers with pre-installed agents (Deploying Veeam Agents Using Generated Setup Files).
Or managed by the agent (Managed by agent), referred to as Backup Policy or Veeam Agent backup job managed by Veeam Agent. A policy is created, which is applied as a template to agents, and the backup job is managed by the agent. It is suitable for computers (laptops) with limited connection to the backup server. If we have a pre-installed Standalone Agent, we must use this mode.

Veeam Agent for Microsoft Windows also supports Backup from Storage Snapshots. The agent must be managed, and we must have integration with the storage array. Veeam Backup & Replication uses Off-host Backup Proxy and Hardware VSS Provider. A native snapshot is created on the storage, and the backup is made from it. Thus, the backed-up computer is much less burdened.
When to Use Veeam Agent
The fundamental question is when it is necessary or advantageous to use the Veeam Agent for backup. With Veeam, finding the answer is quite difficult. There are situations where it is clear. The agent must be used in situations where VM backup cannot be used. For example, for backing up physical computers, VMs in the public cloud, VMs where we cannot create a Snapshot. In practice, I encountered another situation when backing up a VM that uses Raw Device Mapping (RDM), i.e., directly accessing the LUN of the storage array.
In various parts of the documentation, it is stated that an agent is required for backing up a Microsoft Failover Cluster. Supported are Windows File Server Failover Clusters, Windows Server Failover Clusters with SQL, SQL Always On Availability Groups, and Exchange Database Availability Groups. The documentation also lists several limitations (Failover Cluster Support). The agent must be managed by the backup server, the backup job type must be Failover cluster, and the servers must be added using a Protection Group with Active Directory objects and the selected cluster object.
However, it is also mentioned that a basic VM Backup Job can be used for processing virtual clusters without an agent. In the description of Best Practice for backing up Exchange DAG, VM backup without an agent is mentioned.
Agent Backup Job
When backing up with an agent, the agent performs the processing. Depending on the agent mode, the agent needs to communicate with the backup server and always with the backup repository.
Although backing up with an agent works on a different principle than VM backup, almost identical options and settings are available. We will only mention a few differences or notes.
- Computers - we add a Protection Group and/or individual computers (specified by IP address or name, for which we must specify an account - Credentials for access)
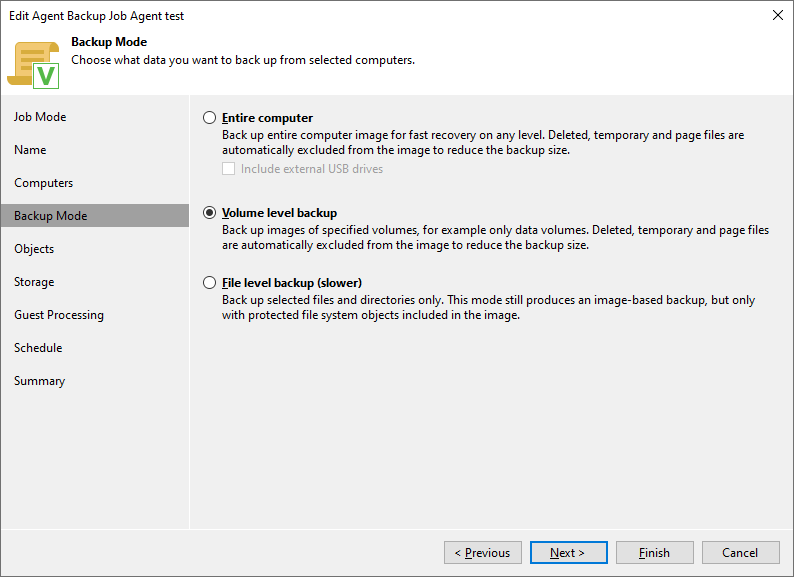
- Backup Mode - we can back up the entire computer (including USB disks, supports CBT and parallel processing), the image of certain volumes (supports CBT and parallel processing), or certain files and folders (less performance, not available for Failover cluster type)
- Guest Processing - the guest processing options are also very similar to those for VMs, but we do not need to specify Credentials for access to the operating system, the permissions under which the agent runs are used for processing
Backup Operations
Renaming a Backup Job
When we create a Backup Job, we assign it a unique name under which the job is displayed in the Veeam Backup & Replication Console. At the same time, a folder with the job name is created in the assigned Repository (in its defined path). For example, D:\Backups\Test VM Backup.
We can easily rename the backup job. We select Edit on it, change the name, and click Finish. However, only the job name changes, and in the History, new sessions are under the new name. The backups are still under the old name, and on the disk, the old folder name remains.
If we want to change everything (to have a logical overview), we can follow the guide How to Move Veeam Backup & Replication Backup Files. It describes situations when moving backup files to new storage, either retaining the backup job or with a new job.
- (not mandatory, but safer) disable the job, Home - Jobs, select Disable on the job to be renamed
- change the job name, select Edit on the job
- in the Repository with the backup, change the folder name containing the backup files (do not change the file names)
- rescan the storage, Backup Infrastructure - Backup Repositories - select Rescan on the storage
- the scan should find and add one new backup and remove one
- when we look at Home - Backups - Disk (Imported), we will see our backup (under the old name), we can check the path by selecting Properties on the backup and then Copy path
- map the backup to the backup job, Home - Jobs, select Edit on the job, on the Storage tab select Map backup, select the backup (still has the original name), complete the wizard (Next) and confirm Apply
- in Home - Backups we see that the backup has disappeared from Disk (Imported) and appeared in Disk under the new name
- enable the job

Moving Backup Files to Another Storage
Note: In version 12, we can already perform the move easily in the console, more in the article Veeam Backup & Replication 12 - Backup Chain and Backup Copy format upgrade (Move backup - moving backups)
- (not mandatory, but safer) disable the job, Home - Jobs, select Disable on the job to be renamed
- move the backup files (the entire folder) to the new Repository
- rescan the new storage, Backup Infrastructure - Backup Repositories - select Rescan on the storage
- the scan finds one new backup, it appears in Home - Backups - Disk (Imported)
- map the backup to the backup job, Home - Jobs, select Edit on the job, on the Storage tab switch the Repository and select Map backup (mapping can be skipped as it should happen automatically), select the backup, complete the wizard (Next) and confirm Apply
- the original files (old Repository) appear in Home - Backups - Disk (Orphaned)
- rescan the original storage, Backup Infrastructure - Backup Repositories - select Rescan on the storage
- the scan removes the backup (Disk (Orphaned) disappears)
- enable the job
Creating a Synthetic Full Backup
- manually (Ad-hoc) only an Active Full Backup can be created
- a Synthetic Full Backup can only be created currently (cannot be created retroactively to a specific Restore Point)
- the only option is to edit the Backup Job, Home - Jobs, select Edit on the job
- set the creation of a Synthetic Full Backup for the current day
- start the job, Home - Jobs, select Start on the job
- revert the change
Another option is to perform an export of the backup in Home - Backups - Export backup. This allows synthesizing a complete and independent full backup file from selected restore points located in the backup repository. This creates a VBK file for a specific date. The function is intended for archiving important restore points, preventing their deletion by Retention Policy and making them portable.
During export, we can select multiple VMs or computers from different types of backups, each machine is saved into an independent Full Backup file. Exported files are saved in the same repository where the restore points are. In Veeam, they are visible under Disk (VeeamZIP) or Object Storage (VeeamZIP). We can set the exported backup to be deleted after a certain period.
Removing Older Restore Points
Removing Missing Restore Points
- delete the selected files on the disk (VIB only makes sense with the corresponding/previous VBK, we must not break the Backup Chain)
- rescan the storage where the backup is, Backup Infrastructure - Backup Repositories - select Rescan on the storage
- let it forget the deleted files, Home - Backups - Disk, select Properties on the backup, the missing Restore Point will be displayed with a red cross, right-click on some and select Forget - All unavailable backups
Dik za clanek. Jen doplnim ze REFS uz neni oficialne podporovany na W10 Pro ( jen asi na workstation edici).
Pro méně náročné je super i ALTARO